The Bitcoin FAQ will allow each of you to find answers to frequently asked questions about the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. It is safe to say that the excitement around it is caused by the frenzied popularity of bitcoin. In order to understand the essence and principles of functioning of this digital currency, one should start with its history and key points. Sooner or later, each of you will face the bitcoin world. This article will help you to become savvy and ready for this meeting.
Contents:
- Bitcoin FAQ. What is bitcoin and who is its creator?
- Who controls the bitcoin network and how does it work?
- How difficult is it to make a Bitcoin payment?
- How Bitcoin is created and how its value is determined?
- Waiting for transaction confirmation and long synchronization process
- Commission for the transaction and receiving bitcoin when the PC is turned off
- What is Bitcoin mining and its help for the Bitcoin safety
- How does Bitcoin mining work?
1. Bitcoin FAQ. What is bitcoin and who is its creator?
1.1. What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin — a consensus network that powers a new payment system and fully digital money. It is the first decentralized peer-to-peer payment network, based on its users, without any central authority or intermediaries. From a user perspective, Bitcoin is a lot like cash on the Internet. It can also be considered as the most outstanding triple-entry accounting system.
1.2. Who is the creator of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin — the first attempt at implementing the concept of “cryptocurrency”, which was first described in 1998 by Wei Dai. In the cypherpunks mailing format, he proposed a completely new form of money that uses cryptography to control its creation and transactions, rather than a central authority. The Bitcoin protocol and software are publicly published and any developer around the world can view the code or create their own modified version of the Bitcoin software. Just like modern developers, Satoshi’s influence was limited to change. Thus, the inventor of Bitcoin is probably as relevant today as the person, who invented paper.
2. Who controls the bitcoin network and how does it work?
2.1. Who controls the bitcoin network?
No one owns the Bitcoin network in the same way that no one owns email technology. Bitcoin is controlled by all Bitcoin users around the world. Despite the fact that the developers improve the software, they are not able to change the Bitcoin protocol forcefully, since all users are free to choose the software and version to use, according to their taste. To remain compatible with each other, all users must use software that follows the same guidelines. Bitcoin can only work correctly with full consensus among all users. Therefore, all users and developers have a strong incentive to defend this consensus.
2.2. How does Bitcoin work?
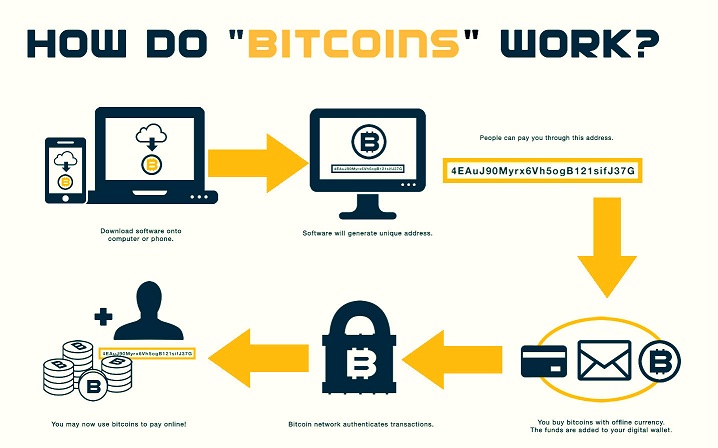
From the user’s perspective, Bitcoin is nothing more than a mobile application or computer program that provides a personal Bitcoin wallet and allows the user to send and receive Bitcoins along with them. This is how Bitcoin functions for many users. The Bitcoin network operates in the format of a public ledger, the so-called “blockchain”. This ledger contains every transaction ever processed, allowing the user’s computer to validate all transactions. All transactions are digitally signed for authentication purposes. These signatures correspond to sender addresses, which allow users to have complete control over sending bitcoins from their personal bitcoin addresses. In addition, anyone can process transactions, using the computing power of specialized equipment and receive bitcoin rewards for this service. This is often referred to as “mining”.
3. How difficult is it to make a Bitcoin payment?
Bitcoin payments are easier to make than payments with a plastic card and this does not require opening a current account. Payments are made through a wallet program, installed on your computer or smartphone, simply by entering the recipient’s address, payment amount and clicking the “send” button. To make it easier to enter the recipient’s address, many wallets can read the address in the form of a QR code or using NFC technology.
4. How Bitcoin is created and how its value is determined?
4.1. Bitcoin creation process
New bitcoins are created in a competitive and decentralized process, called “mining”. This process implies that people are rewarded by the network for their services. The one, who mines actually, processes the transactions and secures the network, using specialized hardware, and gets new bitcoins in return. The Bitcoin protocol is designed in such a way that new bitcoins are created at a fixed rate. This makes Bitcoin mining a very competitive business. As more miners join the network, it becomes more and more difficult to make a profit and miners must find ways to reduce their operating costs.
No central authority or developer has any power to control or manipulate the system to increase their income. Every Bitcoin node will reject any transaction that does not obey the rules that the entire system follows. Bitcoins are being created at an ever decreasing and predictable rate. The number of new bitcoins, created each year, is automatically halved until production stops completely and the total number of issued bitcoins equals 21 million bitcoins. From now on, bitcoin miners will likely be supported solely by a stream of small transaction fees.
4.2. What determines the value of Bitcoins?
Bitcoin price is determined by supply and demand. When demand for bitcoin rises, so does the price, and when demand falls, so does the price. There is a limited number of bitcoins in circulation and new bitcoins are being created at a predictable and ever-decreasing rate, which means that demand must follow this inflation rate for the price to be stable. Since Bitcoin is still a relatively small market, compared to what it might become, it does not take significant amounts of money to move the market price up or down, and, therefore, the price of Bitcoin is still very volatile.
5. Waiting for transaction confirmation and long synchronization process
5.1. Why should you wait for a transaction confirmation?
Receiving a Bitcoin payment is almost instant. However, there is a slight delay before the network begins to validate your transaction, including it in a block, and before you can spend the bitcoins you received. Confirmation means that there is a consensus on the network that the bitcoins you received have not already been sent to someone else and are now considered your property. Once your transaction is included in one block, it will continue to receive confirmations from each subsequent block, which will indicate a strengthening of this consensus and reduce the risk of transaction reversal. Each transaction takes between a few seconds and 90 minutes, with an average duration of 10 minutes. Each user is free to choose at what stage the transaction is considered confirmed, but 6 confirmations are usually considered as safe as 6 months for a credit card transaction.
5.2. What does the “sync” mean, why does it take a long time?
Long synchronization is required only for full-fledged network nodes such as Bitcoin Core. Technically speaking, sync is the process of downloading and verifying all previous bitcoin transactions on the network. Some bitcoin clients need to be aware of all previous transactions in order to calculate the final balance of your wallet and make new transactions. Synchronization can require a lot of computer resources, adequate Internet speed and sufficient disk space to accommodate the full volume of the blockchain. For Bitcoin to remain safe, enough people should use full-fledged Bitcoin nodes because they perform the task of verifying and relaying transactions.
6. Commission for the transaction and receiving bitcoin when the PC is turned off
6.1. How much is the transaction fee?
Transactions can be made without fees, but trying to make a free transaction can slow down the transfer significantly. And while fees can increase over time, they tend to be tiny. By default, all bitcoin wallets, listed on Bitcoin.org, sеlect a suitable fee and give the opportunity to revise it before making a transaction.
Transaction fees are used to guard against users, making transactions to overload the network and as a way of paying miners for their work in maintaining the safety of the network. A more precise purpose of the commissions’ work is still being developed and will change over time. Since the fee is not connected to the amount of sent bitcoins, it can seem incredibly small or unusually high. The commission is determined by parameters such as the data, sent with the transaction, and the repeatability of the transaction. For example, if you receive a large number of small amounts, then the transfer fee will be higher. If your business uses traditional-style transactions, you don’t have to pay high fees extraordinarily.
6.2. What happens if the PC is turned off when receiving bitcoin?
Everything will be OK. You will see bitcoins the next time you launch your wallet program. In fact, bitcoins do not go into the program on your computer, but are added to the public ledger, which is located on all devices on the network. If bitcoins were sent to you when your wallet program is not running and you run it later, it will download the blocks and the bitcoins will eventually appear as if they had just been received. Your wallet should only be launched when you need to spend bitcoins.
7. What is Bitcoin mining and its help for the Bitcoin safety
7.1. What is Bitcoin mining?
Mining — the process of using computer resources to process transactions, ensure network safety and synchronize the state of all users on the system. Mining can be perceived as a Bitcoin data center, except that it was designed to be completely decentralized, with its members, being located in any country, and no one person has control over the network. This process has been called “mining” by analogy with gold mining, because it is also a temporary mechanism, used to issue new bitcoins. However, unlike gold mining, Bitcoin mining generates rewards in exchange for essential services, needed to keep the payment network secure. Mining will still be needed, even after the last bitcoin is released.
7.2. How does mining help the safety of Bitcoin?
Mining creates some semblance of a competitive lottery, which makes it difficult for someone to add all new blocks of transactions to the blockchain sequentially. This protects the neutrality of the network by preventing someone else from blocking any transactions. It also prevents someone from canceling their previous transactions, which can be used to trick other users. Mining makes it exponentially more difficult to reverse previous transactions because it would require recalculating the done work for all blocks, following that transaction.
8. How does Bitcoin mining work?
Anyone can become a Bitcoin miner by running software on specialized hardware. The mining technique listens to the broadcast of transactions through a decentralized peer-to-peer network and performs the necessary tasks to process and confirm these transactions. Bitcoin miners do this job because they can earn transaction fees that users pay to make transactions faster, and newly created bitcoins that are issued, according to an unchanged formula.
For new transactions to be confirmed, they must be included in the block, along with the mathematical justification for the performed work. These proofs are very difficult to create because there is no other way to do it other than by trying millions of calculations per second. Miners perform these calculations until their block is accepted by the system and they receive a reward for it. As more people start mining, the difficulty of finding a new block is automatically increased by the network in order to ensure that the speed of finding one block is on average 10 minutes. As a result, mining is a very competitive business, where no single miner can control what exactly is included in the blockchain.
The proof of work is also dependent on the previous block to ensure chronological order in the block chain. This makes it exponentially more difficult to undo previous transactions because it would require recalculating the work, done for all subsequent blocks. When two blocks appear at the same time, miners work on the first block they received, but switch to the longest blockchain as soon as the next block is found. This allows mining to maintain and protect a global consensus, based on computing power. Bitcoin miners cannot cheat to increase their earnings, nor can they perform fraudulent transactions that can damage the Bitcoin network, because all Bitcoin nodes will reject any block that contains incorrect information, according to the rules of the Bitcoin protocol. Therefore, the network remains safe even if not all Bitcoin miners can be trusted.